In a study that was recently published in Science Advances, laser light therapy was found to be successful in enhancing short-term memory. Researchers from Beijing Normal University and the University of Birmingham in the UK and China showed that non-invasive therapy can increase working memory in persons by up to 25 percent.
A newly developed technology can now produce new-generation multi-point/single-layer superabrasive tools for advanced grinding applications to meet high productivity and energy-efficient material removal requirements. The tools produced also have enhanced tool life.

Scientists have discovered a mechanism by which an area of a protein shape-shifts to convert vitamin A into a form usable by the eye’s light-sensing photoreceptor cells. A previously uncharacterized area of the protein known as RPE65 spontaneously turns spiral-shaped when it encounters intracellular membranes, or thin structures that surround different parts of a cell.
Researchers from IIT-Delhi, in collaboration with AIIMS, have developed the first robotic hand exoskeleton device for rehabilitation of wrist and finger joints for stroke survivors.

The department of haematology at All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Nagpur successfully conducted bone marrow transplants (BMT) for two paediatric patients recently. With this, AIIMS became the first and only government hospital in Maharashtra to have this facility. Vidarbha and central India have a high prevalence of blood disorders like thalassaemia and sickle cell. BMT is the only permanent solution for these blood disorders. The successful BMT at AIIMS with the financial support of government health schemes could be a boon for the poor patients living with these disorders. However, the two surgeries done in AIIMS in the last three weeks were not on thalassaemia patients.
A 39-year-old man underwent a robotic kidney transplant at Safdarjung hospital here, which doctors claimed to be the first such surgery to have been performed at a central government facility in the country.
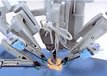
India now has a homegrown robotic surgery system that holds out promise of less prohibitive costs in a niche category of medical treatment, thanks to the efforts of a US returnee cardiac surgeon and his tech team. Designed in India, the SSI Mantra aims to rival the widely popular da Vinci surgical system, which is manufactured by global market leader Intuitive Surgical, and costs less than a third of the latter. The SSI Mantra costs around Rs 4.5 crore and da Vinci Rs 15 crore. It is already being deployed at the Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre in New Delhi, where it was installed last month and has so far performed 22 complex surgeries.
Researchers have developed a gene therapy that rescues cilia defects in retinal cells affected by a type of Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), a disease that causes blindness in early childhood.
In order to study and measure dopamine and serotonin in the human brain, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine have shown that a neurosurgical technique is safe. Their research is available online in the Public Library of Science journal PLOS One.

AIIMS Delhi has come up with a technique that allows patients diagnosed with cancer in the lower part of the body and undergoing tumour removal to have a better life expectancy and good quality of life.

The Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI) has urged the Union government to include indigenously developed cervical cancer vaccine in its immunisation programme and administer the same to girls for free.
Aesthetic procedures including hair transplants should be carried out only by registered medical professionals having adequate training, the National Medical Commission (NMC) said and underlined they should not be attempted by watching demonstrations in workshops or on YouTube.
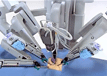
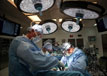
Safdarjung Hospital has become the first central government-run health facility to conduct a robotic cardiothoracic surgery. The hospital, which used the technology for the first time this September, has so far conducted three such surgeries, the authorities said. The technology was procured in October 2019 for gynaecological, urological and cardiothoracic vascular surgeries. “However, in the past two years, the programme couldn’t be started due to Covid-19. In India, there was no such established cardio programme when we bought the robotic technology. Even now, only a few hospitals have it,” said Dr Anubhav Gupta, head of the department of cardiothoracic vascular surgery (CTVS).
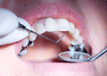
People who are at high risk of developing a life-threatening heart infection should be given antibiotics before undergoing invasive dental procedures, according to new research from the University of Sheffield. These results suggest that current NICE guidelines, advising against routine use of antibiotics before invasive dental procedures for those at high IE-risk, should be reconsidered. The study, led by Professor Martin Thornhill from the University’s School of Clinical Dentistry, suggests that current UK guidelines against the use of antibiotics, issued by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), could be putting high-risk patients at unnecessary extra risk when undergoing invasive dental procedures. At the same time, the results validate guidance in the USA, Europe and elsewhere that recommend that those at high-risk are given antibiotics before invasive dental procedures.

AIIMS Delhi has started conducting tests of samples collected to detect monkeypox virus. The AIIMS virology lab under the microbiology department is one of the 15 labs authorised across the country for the test by the department of health research-Indian Council of Medical Research.

AIIMS Delhi on Thursday announced a raise in the charges of its private ward rooms. The move comes following a recent decision by the GST Council to levy a 5 percent tax on hospital room rent exceeding Rs 5,000 per day. The revised charge will be effective from July 18, as per government notification.

Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is offering new hope to patients of chronic pain such as back pain, neck pain, facial pain, and joint pain like that of shoulder and knee. The technique was in the limelight recently when tennis star Rafael Nadal underwent the procedure to cure his chronic foot pain after all other treatment options failed.

Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Center (RGCI), New Delhi gets its first-ever Made-in-India Surgical Robotic System, SSI-Mantra which is developed by med-tech start-up SS Innovations. On Thursday, robotic cardiac surgeon Dr. Sudhir P Srivastava and creator of SSI Mantra, along with Dr. Sudhir Rawal, Medical Director, RGCI announced the official launch and acquisition of the first model of the indigenous surgical robotic system. The Gurugram-based company claims that it is cheaper, more advanced, and more efficient than the US FDA-approved Da Vinci system which was approved for use in India in 2000. In 2002, India’s first robotic cardiac surgery was conducted with the Da Vinci system, and the first urological surgery in 2006.

In a study that was recently published in Science Advances, laser light therapy was found to be successful in enhancing short-term memory. Researchers from Beijing Normal University and the University of Birmingham in the UK and China showed that non-invasive therapy can increase working memory in persons by up to 25 percent.

A newly developed technology can now produce new-generation multi-point/single-layer superabrasive tools for advanced grinding applications to meet high productivity and energy-efficient material removal requirements. The tools produced also have enhanced tool life.

Scientists have discovered a mechanism by which an area of a protein shape-shifts to convert vitamin A into a form usable by the eye’s light-sensing photoreceptor cells. A previously uncharacterized area of the protein known as RPE65 spontaneously turns spiral-shaped when it encounters intracellular membranes, or thin structures that surround different parts of a cell.

Researchers from IIT-Delhi, in collaboration with AIIMS, have developed the first robotic hand exoskeleton device for rehabilitation of wrist and finger joints for stroke survivors.

The department of haematology at All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Nagpur successfully conducted bone marrow transplants (BMT) for two paediatric patients recently. With this, AIIMS became the first and only government hospital in Maharashtra to have this facility. Vidarbha and central India have a high prevalence of blood disorders like thalassaemia and sickle cell. BMT is the only permanent solution for these blood disorders. The successful BMT at AIIMS with the financial support of government health schemes could be a boon for the poor patients living with these disorders. However, the two surgeries done in AIIMS in the last three weeks were not on thalassaemia patients.

A 39-year-old man underwent a robotic kidney transplant at Safdarjung hospital here, which doctors claimed to be the first such surgery to have been performed at a central government facility in the country.

India now has a homegrown robotic surgery system that holds out promise of less prohibitive costs in a niche category of medical treatment, thanks to the efforts of a US returnee cardiac surgeon and his tech team. Designed in India, the SSI Mantra aims to rival the widely popular da Vinci surgical system, which is manufactured by global market leader Intuitive Surgical, and costs less than a third of the latter. The SSI Mantra costs around Rs 4.5 crore and da Vinci Rs 15 crore. It is already being deployed at the Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre in New Delhi, where it was installed last month and has so far performed 22 complex surgeries.

Researchers have developed a gene therapy that rescues cilia defects in retinal cells affected by a type of Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), a disease that causes blindness in early childhood.

In order to study and measure dopamine and serotonin in the human brain, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine have shown that a neurosurgical technique is safe. Their research is available online in the Public Library of Science journal PLOS One.

Teens with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) who took bromocriptine, a medication used to treat Parkinson’s disease and Type 2 diabetes, had lower blood pressure and less stiff arteries after one month of treatment compared to those who did not take the medicine, according to a small study published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal.

Every one-year increase in retinal age has now been linked with a 10 percent higher risk of incident kidney failure over 11 years of follow-up, a UK study involving 35,864 residents has revealed. The one-year increase in retinal age was assessed by retinal microvasculature changes, according to the study published in the Peer-reviewed American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD).

Contact lenses are pretty common. But ever heard of smart contact lenses? An international team of scientists from India and the UK has developed a ‘smart contact lens’ to test for eye infections. According to scientists, the test can detect infection in a quick and non-invasive way. The University of Sheffield along with the University of Bradford and the LV Prasad Eye Institute in India hope the test could eventually be available to use at home and has been hailed as the next big leap in the global fight against preventable blindness.
Long Covid patients experience several of the same lingering negative effects on their physical, mental, and social well-being as those experienced by people who become ill with other, non-Covid illnesses, new research has revealed. The researchers found that 40 percent of the Covid-positive and 54 percent of the Covid-negative group reported moderate-to-severe residual symptoms three months after enrolling in the study.

Scientists have discovered a new material that can be applied to wounds">diabetic wounds for faster healing with just one application. Researchers from the University of Nottingham have discovered a new class of polymer that can provide instructions to both immune and non-immune cells to aid healing in hard-to-treat wounds">diabetic wounds. The findings have been published in Advanced Materials.

Engineered immune cells, known as CAR T cells, have shown the world what personalized immunotherapies can do to fight blood cancers. Now, investigators have reported highly promising early results for CAR T therapy in a small set of patients with the autoimmune disease lupus. Penn Medicine CAR T pioneer Carl June, MD, and Daniel Baker, a doctoral student in Cell and Molecular Biology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, discuss this development in a commentary published today in Cell.

A recent study by researchers from NIMHANS has found an earlier onset of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in Indians compared to people living with this movement disorder in other countries. This difference extends to almost a decade, revealed the study that has been published in ‘Parkinsonism and Related Disorders’ last week. Pramod Kumar Pal, Professor, Department of Neurology at NIMHANS, who is the corresponding author of the study, said that a manual chart review was carried out for 2,035 patients, including 550 women, with PD who had been evaluated at the Neurology OPD and Movement Disorder Clinic at NIMHANS.

For decades doctors have been telling their patients that high levels of HDL, otherwise known as “good cholesterol,” could protect them from heart disease. But a new study suggests that having a lot of so-called good cholesterol doesn’t mean a lower risk of heart attacks. That doesn’t mean HDL levels have no impact. An analysis of data from nearly 24,000 American adults revealed that too little HDL cholesterol was associated with an increased risk of heart disease — in white adults, but not in Black adults, researchers reported Monday in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.

University of Chicago scientists announced the development of a novel method for creating synthetic molecules capable of targeting these previously ‘untargetable’ transcription factors. While known for a long time that tumours use these proteins to grow out of control, their unique configurations meant that they had earned the moniker ‘undruggable’ for more than 30 years. University of Chicago made a breakthrough while cancer researchers worldwide have been looking for a way to target transcription factors for decades.

Assam Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma on Saturday inaugurated the second ultramodern radiotherapy unit in the cancer care centre of Health City Hospital in Guwahati.

When you donate blood, it is not transfused into a needy patient directly. The donated blood, also referred to as whole blood, is processed or spun in centrifuges to separate it into transfusable components. This includes red cells, platelets, and plasma. The exercise is referred to as blood processing and it comes at a cost. In order to standardise charges and put a cap on it, the Centre has recently released a detailed guideline. It states that private blood banks cannot charge more than Rs 1,550 for processing whole blood.

Life altering moments like pregnancy, birth, and early parenthood can be stressful for women and their partners. As a result, women may undergo a period of poor mental health or witness a worsening of previous mental health conditions.
Union Health Minister Mansukh Laxmanbhai Mandaviya on Friday said that a web portal has recently been created to provide information on the blood types available in the banks across the country, thus giving a momentum to the voluntary blood donation movement.

GE Healthcare on Monday announced the launch of its first ‘Made in India’, ‘AI-powered’ Cath lab – Optima IGS 320 to advance cardiac care in India. According to the company’s press statement, the Cath lab is built at Wipro GE Healthcare’s new factory launched under the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme in Bengaluru. In India, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) contribute to 60 percent of all deaths, of which, 82 percent occur due to cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), chronic respiratory diseases, cancer, and diabetes.
With India facing a huge disease burden of kidney dialysis patients, the National Medical Commission (NMC) has directed all medical colleges to strictly implement the Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Portal to cater to the needs of patients who meed expensive dialysis services. With this, the union government aims to focus on expanding the coverage of Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme (PM-NDP) with a provision of free dialysis services to the poor in all the states/UTs.

The Union health ministry has issued draft guidelines, proposing annual health check-ups, a creche facility and work hours not exceeding 40 in a week, among other measures, to improve the working conditions of nurses in all healthcare institutions. It has also recommended that all healthcare establishments may, as far as possible, provide accommodation to their nursing staff within or near their premises.
Based on the recommendations made by the National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI), the interval between the second and the precaution dose of COVID-19 vaccines was revised from nine months to six months for all beneficiaries aged 18 years and above from July 6, the government informed Parliament on Friday. In a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha, Minister of State for Health Bharati Pravin Pawar said as on August 1, a total of 9.07 crore (13 percent) precaution doses of the Covid vaccines were administered against the due beneficiaries.

A new portal that captures detailed information on the data related to tuberculosis from all over the country and would be accessible to everyone is going to be launched soon, Union Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya has said.

The Union health ministry has notified the inclusion of coronary stents in the National List of Essential Medicines, 2022, a move that will help make these life-saving medical devices more affordable. The move is based on the recommendations by an expert committee constituted to review the inclusion of stents in the list based on requirement. The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) will now fix the price of coronary stents. On November 6, the Standing National Committee on Medicines (SNCM) had submitted its recommendation for inclusion of coronary stents in the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM), 2022 in two categories—Bare Metal Stents (BMS) and Drug Eluting Stents (DES) which include metallic DES and bioresorbable vascular scaffold (VBS)/biodegradable stents.
Biological E (BE), a Hyderabad-based vaccine and pharmaceutical company, has recently announced the publication of CORBEVAX COVID-19 vaccine phase II/III clinical trials conducted in paediatric population (5 to <18 age group). The vaccine has demonstrated excellent safety profile in children and adolescents. The vaccine also demonstrated excellent immunogenicity as measured by humoral and cellular immune responses. Dr Vikram Paradkar, Executive Vice President-Technical Operations, Biological E. Limited, said, “CORBEVAX getting approved for our paediatric population from 5 to 18 age-group was a major milestone for us and its subsequent Pan-India deployment for kids of 12-14 years was important in our fight against coronavirus. So far, approximately 74 million doses of CORBEVAX has been administered to kids in India and almost 33 million kids have completed two-dose primary vaccination, which represents one of the largest paediatric campaigns globally. We plan to eventually test the vaccine on infants as young as six months, based on the excellent safety record and consistent immunogenicity observed in paediatric trials and deployment."
Data on the vaccine was reviewed and discussed by SAGE (Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunisation), but a decision has been paused until a final decision is made on the vaccine that is in the process of seeking an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the WHO, Dr Joachim Hombach, Executive Secretary , SAGE (WHO) said. The group is in touch with the manufacturer, he said, adding that they were seeking data in relation to the vaccine use in India. SAGE and the Technical Advisory Group (TAG) evaluate evidence on the vaccine, but from two different perspectives. The policy recommendations made are contingent on the second technical component of the review process involved in approving a vaccine for an EUL.

To help people with type-1 diabetes who need to take insulin regularly to avoid low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) or high blood sugar (hyperglycaemia), a team of researchers has developed an artificial pancreas system that can monitor and control blood sugar levels in real time.

A made-in-India artificial heart or left ventricular assist device (LVAD) will be a reality soon, with a team of IITians and investors from across the country working on it. The device will be available for just Rs 20 lakh, compared to the Rs 1.20 crore cost of an imported artificial heart.

The apex health research body of the country, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), has got a new head, with the appointments committee of the Cabinet appointing Rajiv Bahl, a senior World Health Organisation researcher, as its director general. Bahl is the head of research on maternal and newborn child, adolescent health and aging at the World Health Organisation (WHO). Apart from being the DG, ICMR, he will also be the secretary, department of health research (DHR). Bahl joined WHO in 2003 and currently coordinates research and guidelines development in the areas of maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health.

The new ARTIS icono systems adapts flexibly to the differing needs of cardiovascular interventions, interventional radiology, neuroradiology, and vascular interventions. In addition to the multidisciplinary approach, connectivity and digitalisation of interventional labs are becoming increasingly important. The ARTIS icono provides a interface to enable system parameters to be shared easily with devices from other manufacturers with its third-party broker solution.

Engineers at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Stanford University have developed a small, self-contained device with a stretchable/flexible sensor that can be adhered to the skin and used to measure the changing size of tumours below. With the press of a button, the non-invasive, battery-powered device can wirelessly beam results to a smartphone app in real time.

Four key anti-cancer drugs and four patented antivirals used in the treatment of tuberculosis, HIV and hepatitis C are set to get cheaper with their inclusion in the latest edition of National List of Essential Medicines, 2022, published on Tuesday. The list features 384 medicines as against 376 in NLEM, 2015. It adds 34 medicines and deletes 26 from the previous list. The 34 new medicines in NLEM, 2022, feature four anti-cancer drugs so far in the non-scheduled drug category and hence are expensive. These include injections and tablets used in the treatment of cancers of white blood cells, pancreas, prostate and bone marrow. With these additions today, NLEM, 2022, has 63 anti-cancer medicines which are now under price control and affordable.
A meta-analysis of 23 studies, including 854 patients aged 12 to 20 years with mRNA vaccine-associated myopericarditis (rare acute heart inflammation), has found that the incidence of myopericarditis was higher in males after the second dose, adding that however, the overall cases are very low. The findings, published in JAMA Pediatrics, a journal of JAMA Network, suggest largely low incidence rates and favourable outcomes of Covid vaccine-associated myopericarditis in adolescents and young adults.
According to a study, myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was rare but higher in younger males, particularly after the second mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine, implying that vaccine type, age, and gender should all be taken into consideration when vaccinating.
An expert group of the World Health Organization is set to review Biological E’s data on its Covid-19 vaccine, Corbevax, this week. The data review follows BE’s application for an Emergency Use Listing for Corbevax. An EUL paves the way for more countries to include the vaccine in their innoculation programmes. And if, indeed, Corbevax eventually gets a go-ahead from the WHO, it would be the third vaccine company from India, after Serum Institute and Bharat Biotech, to get an EUL on their Covid-19 vaccine. The Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunisation (SAGE)’s four-day meeting starts on Monday with the review of several issues, including the global polio eradication programme. The evidence review for Corbevax is slated for October 5th. According to the WHO draft agenda, SAGE would formulate policy recommendations for this vaccine in case it gets the green-light at a later date. Explaining the significance of an EUL when the WHO itself has indicated that the end of the pandemic was in sight, BE’s Dr Vikram Paradkar, Executive Vice President (Manufacturing & Technical Operations), said an EUL was a major milestone for any Covid-19 vaccine, especially in terms of meeting quality bench-marks. “Vaccines are still being used in many parts of the world and have expanded to different sections of the population. Having an EUL is essential for any vaccine to be deployed to different parts of the globe,” Paradkar said.
A study funded by the US government has tried understanding if the aluminum in children vaccine tends to affect and cause asthma and other allergies in the toddlers. The aluminum is an additive used in children vaccine. Aluminum has been used in some vaccines since the 1930s, as an ingredient — called an adjuvant — that provokes stronger immune protection.

A team of researchers at the Manipal-based Kasturba Medical College (a constituent of Manipal Academy of Higher Education) which looked into changes in sperm quality in men after receiving Covishield vaccine have found that their fertility was unaffected. The research was published on September 5 in the official journal of the UK-based Society for Reproduction and Fertility.
International Pharmaceutical Federation (FIP) has now issued a new guidance on “Optimising vaccination through co-administration of influenza and Covid-19 vaccines’ Vaccination is a key strategy in the prevention of respiratory infectious diseases like Covid-19 and influenza, and therefore improves people’s quality of life. Administering vaccines against Covid-19 and flu at the same time increases uptake of each vaccine and increases protection against both diseases, said FIP.
People aged above 18 years are taking Corbevax as a precaution Covid-19 dose with great enthusiasm. In the state, around 32 percent of the doses administered as precaution doses were Corbevax vaccines, which means that 32 percent of the people who had received first two doses of Covishield or first two doses of Covaxin opted for Corbevax as a precautionary dose as they did not receive Covishield or Covaxin as precautionary doses. The government had approved Biological E's Corbevax as a precautionary dose on August 10. Since then, 19,73,313 Corbevax doses have already been used as precautionary doses.
Vaccinated people who were infected by the first Omicron subvariants have four times greater protection than jabbed people who did not catch the COVID-19 infection, according to a study. The research, published recently in the New England Journal of Medicine, analysed the probability of vaccinated people becoming infected with the subvariant BA.5 currently in circulation. The researchers in Portugal estimated the degree of protection conferred by infections with previous variants and used real-world data. “Vaccinated people who were infected by Omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.2 have a protection against infection with subvariant BA.5, in circulation since June, about four times greater than vaccinated people who were not infected at any time,” said Luis Graca, a professor at the University of Lisbon.

The Central government launched India first vaccine against cervical cancer--Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus vaccine (qHPV), has been developed by the Serum Institute of India (SII) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) on Thursday. According to the Serum Institute, the vaccine is likely to cost 200-400 per dose. Adar Poonawalla, CEO, Serum Institute of India said “We will announce the price of the vaccine in a few months. It will be around ₹200-400. We will start production by November and December and final decision on rates will be discussed with the government."

Statins may do more than help your heart: New research shows the cholesterol-lowering drugs may also lower your risk for a bleeding stroke. An intracerebral hemorrhage, which involves bleeding in the brain, comprises about 15 percent to 30 percent of strokes, according to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. It is also the most deadly. With this type of stroke, arteries or veins rupture, and the bleeding itself can damage brain tissue. The extra blood in the brain may also increase pressure within the skull to a point that further harms the brain.

Everyone is familiar with a cancer survivor. Around 10 million deaths and 19 million new cases were reported globally in 2020. Although treatments are constantly being improved, they can still harm healthy cells or have unpleasant side effects that are difficult for patients to deal with.

Dolutegravir (DTG), the wonder drug recently added to the basket of medicines to treat HIV in the country, is causing weight gain, diabetes, hypertension and sleep disorders, according to several of its users. While the drug has been lauded for having fewer side effects in comparison to previous regimens, it is leading to dropouts in a section of younger patients because of the after-effects.

A new study has revealed that a small molecule inhibitor that attacks the difficult-to-target, cancer-causing gene mutation KRAS, found in nearly 30 percent of all human tumours, successfully shrunk tumours or stopped cancer growth in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. The study was published in the journal, 'Cancer Discovery'.

According to a new study by Penn Medicine researchers, ketamine, an established anaesthetic and increasingly popular antidepressant, dramatically reorganises activity in the brain, as if a switch was flipped on its active circuits.

A new, single-dose oral treatment for sleeping sickness is 95 percent effective in adults and adolescents, regardless of disease stage, and could be a key factor in eliminating disease transmission by 2030, according to a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Developed by not-for-profit Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) and Sanofi, acoziborole, unlike current treatments for sleeping sickness, does not require multiple days of treatment, hospitalisation or highly skilled health personnel, the researchers said.

A single drug compound simultaneously attacks hard-to-treat prostate cancer on several fronts, according to a new study in mice and human cells. It triggers immune cells to attack, helps the immune cells penetrate the tumour, and cuts off the tumour’s ability to burn testosterone as fuel, according to new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The drug may offer a promising new strategy for treating patients whose tumours don't respond to standard therapy.

A drug used to treat high blood pressure was found to be ineffective in treating even mild COVID-19 cases, according to a study based on ‘real world’ data from India. Scientists, from London School of Hygiene, University of Oxford and TPP House, UK, have provided ‘real world’ evidence on the effectiveness of COVID-19 treatments, through two studies, helping shed more light on whether the drugs used to treat covid cases can prevent people from becoming seriously ill. One of the studies, which are published in the British Medical Journal, is based on data from India and involves angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or drugs widely used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease, including telmisartan. The study is a randomised controlled trial involving 787 patients, 778 from India and nine from Australia, with an average age of 49 years, admitted to hospital from May 2020 to November 2021. Included patients had predominantly mild disease, although the researchers aimed to recruit patients at risk of severe covid, the study said.

Research in Africa found a one-time dose of an experimental drug protected adults against malaria for at least six months, the latest approach in the fight against the mosquito-borne disease. Malaria killed more than 620,000 people in 2020 and sickened 241 million, mainly children under 5 in Africa. The World Health Organization is rolling out the first authorized malaria vaccine for children, but it is about 30 percent effective and requires four doses. The new study tested a very different approach — giving people a big dose of lab-made malaria-fighting antibodies instead of depending on the immune system to make enough of those same infection-blockers after vaccination.
Disclaimer: This news page has curated abstracts of daily healthcare news stories from various daily news outlets. To view the complete story, click on the link (provided with each news). Biological E Limited in collaboration with TodaySource has not verified these news stories and are not liable for the authenticity of the news.
If you choose to provide us with your email address or any other personally identifiable information, we will use it only to send you our newsletter or respond to your query.